Cross Sectional Area Of Sphere
Of all shapes, a sphere has the smallest expanse for its volume.
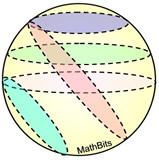
• A cracking circle is the largest circumvolve that can exist fatigued on a sphere. Such a circle volition be plant when the cross-sectional aeroplane passes through the center of the sphere.
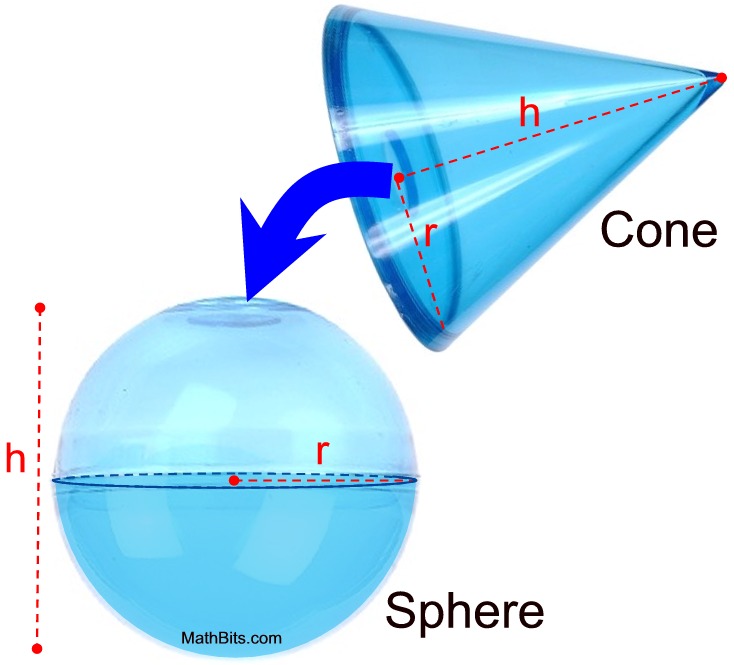
Volume of a Sphere: Annotation: The volume of a sphere is actually the volume of the solid inside a sphere, frequently referred to as a spherical solid. The volume inside of a sphere is four-thirds times π, times the cube of its radius.
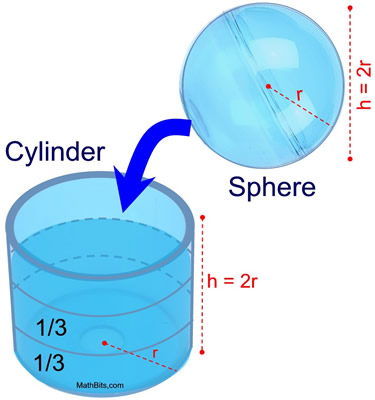
Justification of formula past "cascade and measure" (sphere/cylinder):
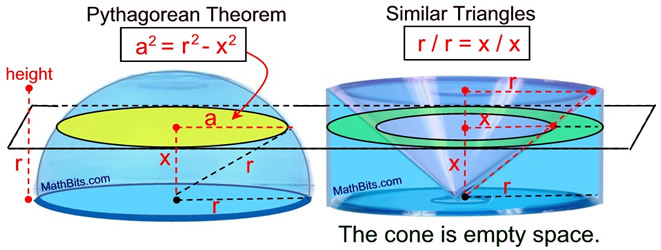
Justification of formula by "Cavalieri's Principle": Now, we know that the volume of a cone is ane-third the volume of a cylinder (of aforementioned radius and pinnacle).
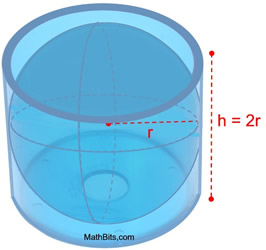
The volume of the new one-half-sphere will equal the volume of the new half-cylinder minus the volume of a right circular cone of radius r and elevation r. The cone is placed inside the cylinder, as shown. The volume of the infinite remaining in the half-cylinder equals the volume of the half-sphere.
The conditions of Cavalieri's Principle are met and the plane parallel to the bases intersects both regions in cross-sections of equal area. The regions nosotros examined have equal volumes . The surface expanse of a sphere is 4 times the area of the largest cross-sectional circle, called the nifty circle.
See applications of spheres under Modeling. Annotation: The re-posting of materials (in role or whole) from this site to the Internet is copyright violation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cross Sectional Area Of Sphere,
Source: https://mathbitsnotebook.com/Geometry/3DShapes/3DSpheres.html
Posted by: couturedoemput.blogspot.com


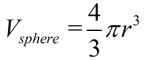
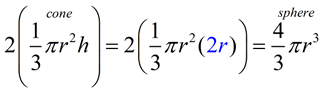
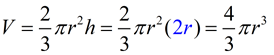 .
.


0 Response to "Cross Sectional Area Of Sphere"
Post a Comment